
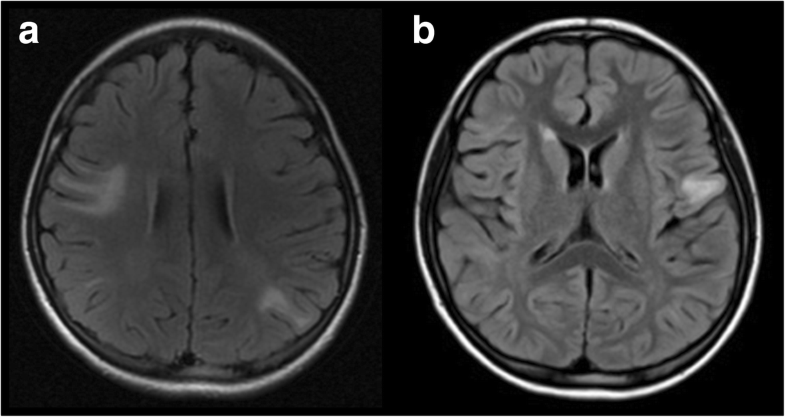
In most of the previous retrospective cross-sectional studies, the final visual outcome was assessed after 3 months or more from ON onset, but the length of the follow-up period was inconsistent between the different disease groups. The long-term neurological prognosis after more than several years from onset or risk factors deteriorating the neurological outcomes in MOGAD has not yet been fully determined.
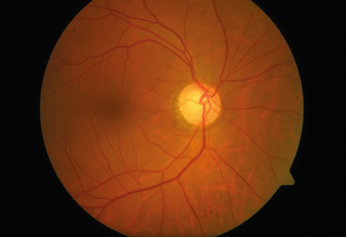
Meanwhile, there are small fractions of patients with MOGAD who present with severe neurological sequelae despite appropriate acute and chronic treatments (Akaishi et al., 2016 Reindl et al., 2017). Many previous studies reported that the visual prognosis after ON in anti-AQP4-positive NMOSD is generally worse than that in MOGAD or MS, although relapses are not rare in MOGAD (Akaishi et al., 2016 Deschamps et al., 2018 Ishikawa et al., 2019 Jitprapaikulsan et al., 2018 Liu et al., 2019). Some previous studies have reported that the resulting irreversible neurological disability levels after myelitis were significantly worse in anti-AQP4-positive NMOSD than in other conditions (Höftberger et al., 2015 Mariano et al., 2019). Neurological sequelae caused by attacks are generally considered to be more severe with irreversible neurological disability in anti-AQP4-positive NMOSD than in MOGAD or MS (Akaishi et al., 2020a Chen et al., 2018 Jarius et al., 2014). The most common phenotype of MOGAD includes ON and myelitis (Hor et al., 2020 Jarius et al., 2016), but cerebral and/or brainstem lesions with a phenotype similar to acute disseminated encephalomyelitis can also be observed (Ogawa et al., 2017 Reindl and Waters, 2019). Similar to anti-AQP4-positive NMOSD, patients with MOGAD typically present with single or recurrent episodes. MOGAD is a recently emerging concept, characterized by the presence of anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) antibodies in the serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (Akaishi et al., 2021), and presents with different demographic and clinical features from those in MS (Di Pauli and Berger, 2018 Fujihara, 2020). Optic neuritis (ON) is a major clinical attack phenotype in demyelinating neurological diseases of the central nervous system, including multiple sclerosis (MS), anti-aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), and anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated disease (MOGAD) (Sato et al., 2014 Wingerchuk et al., 2015).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
